This guide walks you through designing precise and scalable segments in Dynamics 365 Customer Insights Realtime Journeys. Explore attribute-based filters, behavioral triggers, related table connections, and nested segments. Learn limitations, tips, and best practices to optimize audience targeting real-time journeys and data-driven marketing campaigns.
What This Guide Covers
Attribute based segmentation
Behavioral segmentation
Related table segmentation
Nested segment usage
Real world scenarios and considerations
Limitations in Customer Insights
Best practices
Segment refresh behavior
Who This Is For
Dynamics administrators
Marketing teams
Customer Insights implementers
Solution architects
Data analysts
Context & Problem Statement:
Why Leading Organizations Choose Dynamics 365 Customer Insights for Advanced Segmentation?
Modern organizations depend on accurate segmentation to deliver meaningful and timely customer experiences. Dynamics 365 Customer Insights, through its Realtime Journeys app, provides a smart and flexible platform for building audiences and automating campaigns. Unlike earlier approaches, such as the older Outbound Marketing module, Realtime Journeys offers more advanced, dynamic, and scalable capabilities. Many teams, however, still face challenges when working with dynamic dates, behavioral signals, related records, or multi-value attributes.
When segmentation is not designed correctly, teams can encounter inconsistent audiences, duplicated journeys, increased maintenance effort, and delays caused by manual updates. On the other hand, by taking full advantage of Realtime Journeys’ filters, relationship paths, and dynamic criteria, organizations can scale audience management efficiently and deliver personalized communications across marketing, service, and automation.
This guide walks through key segment types, real-world examples, platform considerations, and best practices to help teams get the most out of Customer Insights Journeys. The focus is on keeping segmentation flexible, reliable, and aligned with business goals, while making recurring and dynamic journeys easier to manage.
Prerequisites and Licensing Overview
To use segmentation effectively in the modern Realtime Journeys app within Dynamics 365 Customer Insights Journeys, it is important to understand the licensing, required capacity, and environment readiness.
License Model
Customer Insights works on a tenant capacity model. Instead of individual user seats, organizations receive capacity in two forms:
Interacted People
Used by Customer Insights Journeys for marketing and communication activities.
Unified People
Used by Customer Insights Data to store customer profiles and unify records across sources.
The base license typically includes ten thousand Interacted People capacity and one hundred thousand Unified People capacity. Additional capacity can be added depending on business needs.
Service Limits and Segment Performance
Large numbers of active segments or extremely complex segment criteria may affect refresh performance. Microsoft recommends periodic cleanup of unused segments to maintain an efficient system.
Environment and Permissions
Customer Insights requires a Dataverse environment with proper admin permissions, the ability to install solutions, and support for necessary system users. These system accounts should remain intact to allow the product to operate accurately.
User Access
Users with appropriate security roles can work with segmentation even without consuming a paid seat through an available free user license that grants access to Customer Insights capabilities.
Step-by-Step Implementation
Creating Segments
Navigate to Customer Insights → Audiences → Segments → New Segment.
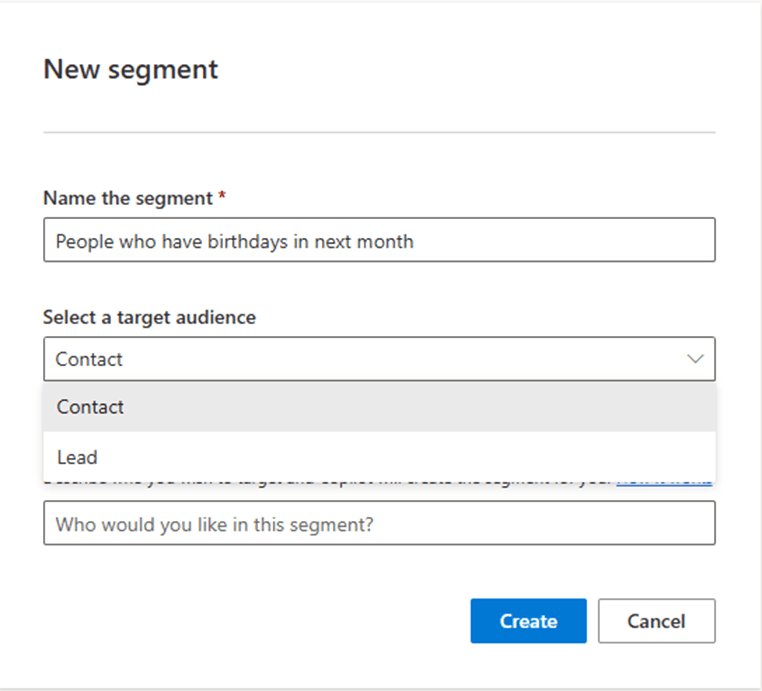
Name your segment and select your primary entity: Contact or Lead.
Quick Comparison of Segment Types (2025)
Segment Type | Primary Use Case | Refresh Frequency | Supports Related Entities? | Nestable? |
Attribute-based | Demographics, firmographics, static data | ~30 min | No | Yes |
Behavioral | Email opens, clicks, form submits | ~60 min | No | Yes |
Related record | Purchases, subscriptions, cases, custom entities | ~30 min | Yes | Yes |
Nested Segment | Combine any existing segments using (AND/OR/NOT) | Depends on children | Depends | No (only 1 level) |
Segment Types with Simple Examples
Attribute-Based Segment
Attribute-based segments allow users to filter records based on values directly stored on a profile entity. This is one of the most used segment types because it works with clean and structured profile data.
Filtration Options by Field Type
- Text fields support contains, equals, starts with, or ends with, useful for filtering names, categories, or status values.
Number fields allow equals, greater than, less than, or in range, suitable for scores, quantities, or numeric thresholds.
Date fields can be filtered using before, after, between, or relative ranges, perfect for birthdays, anniversaries, subscription renewal dates, or other time-based events.
Choice fields support equals, does not equal, or in list, ideal for statuses, departments, or predefined categories.
Boolean fields can be filtered by true or false, helping target customers based on flags like Is Active, Is Verified, or Opt In.
Lookup fields allow filtering based on association or non-association with related entities such as Vendor, Asset, or Account, enabling segmentation across related tables.
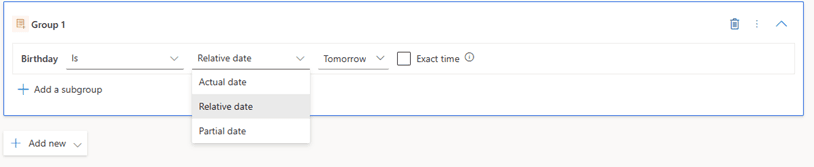
Example: Finding Customers with Birthdays tomorrow.
Using the Date of Birth field, Customer Insights provides three helpful date filtering methods:
Relative Date allows selecting values such as tomorrow or the next thirty days
Actual Date applies a specific calendar value
Partial Date allows matching only day or month regardless of year
This approach ensures precise targeting, reduces manual effort, and helps create dynamic, automated campaigns in Customer Insights.
Behavioral Segment
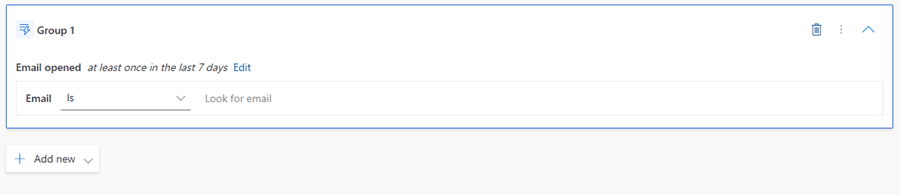
Behavioral segments use real interaction data from Customer Insights Journeys. They enable targeting of customers based on engagement patterns, such as email opens, clicks, form submissions, or other actions.
A typical use case is identifying customers who opened an email in the last seven days.
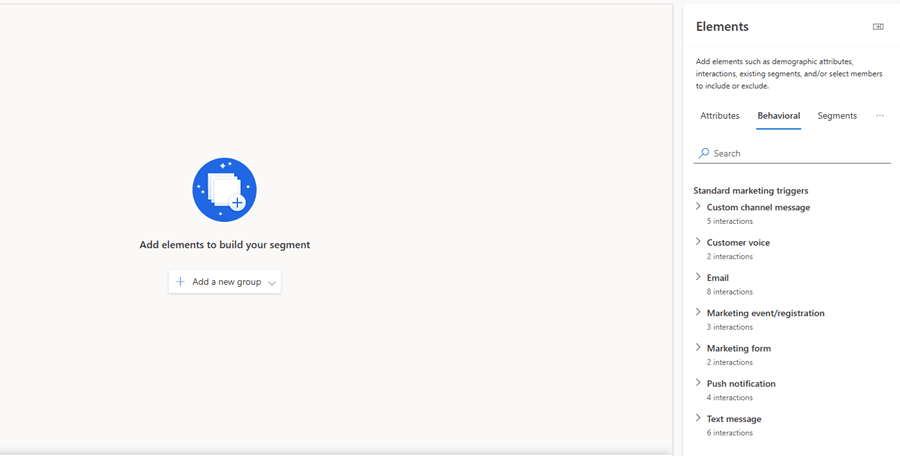
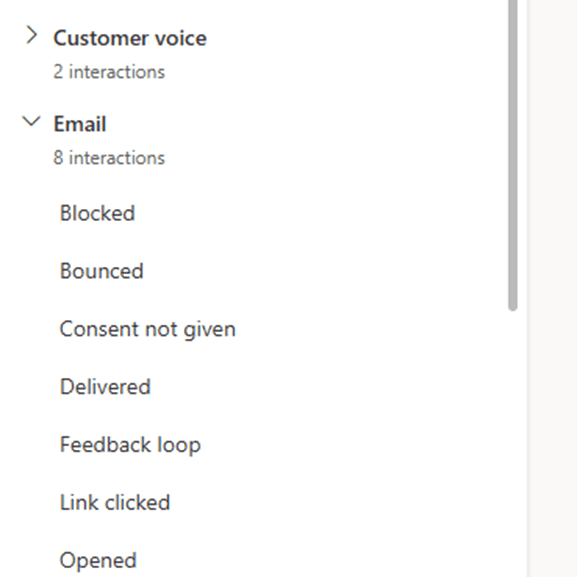
How it appears in CI
Select Behavioral under the elements pane to explore prebuilt engagement triggers. These include email interactions, link clicks, form submissions, and other marketing activity events that can be used to build precise behavioral audiences.
Using Related Tables for Segmentation
Related table segmentation is useful when targeting customers based on information stored in another table. Instead of filtering only on the primary entity, users can navigate through relationships to build richer segment logic.
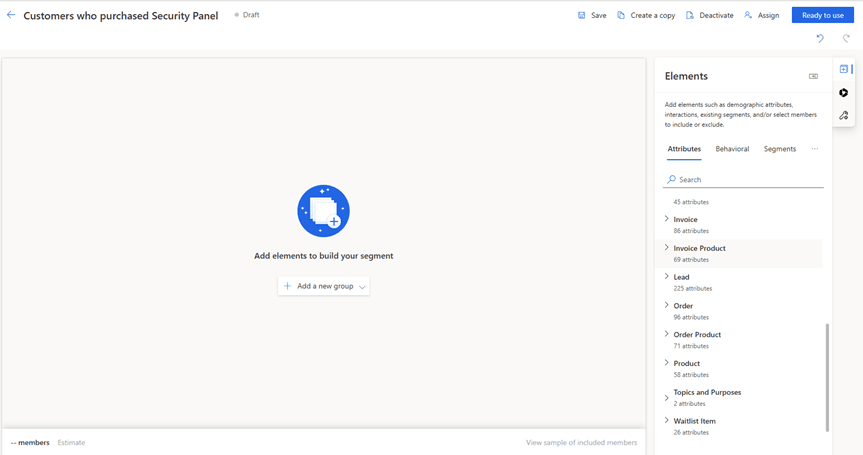
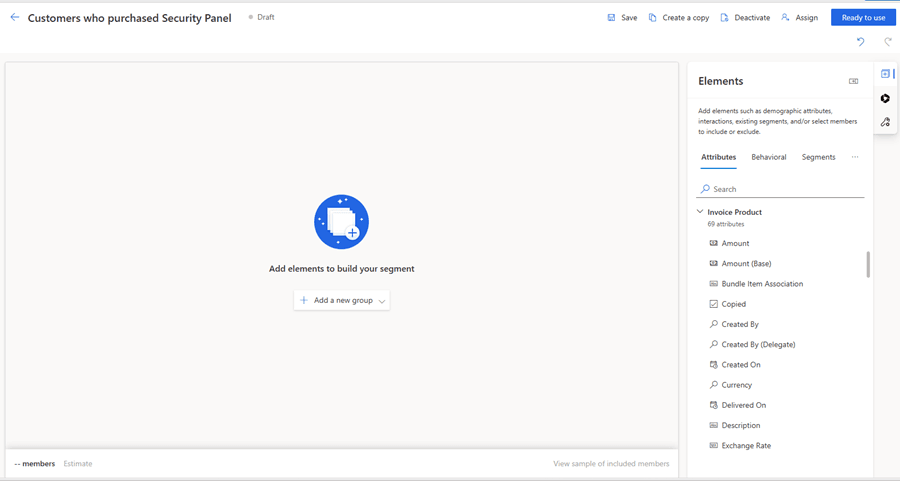
Example: Finding Customers Who Purchased a Specific Product
In this example, we will create a segment starting from the Invoice Product table and filter contacts based on the products they purchased.
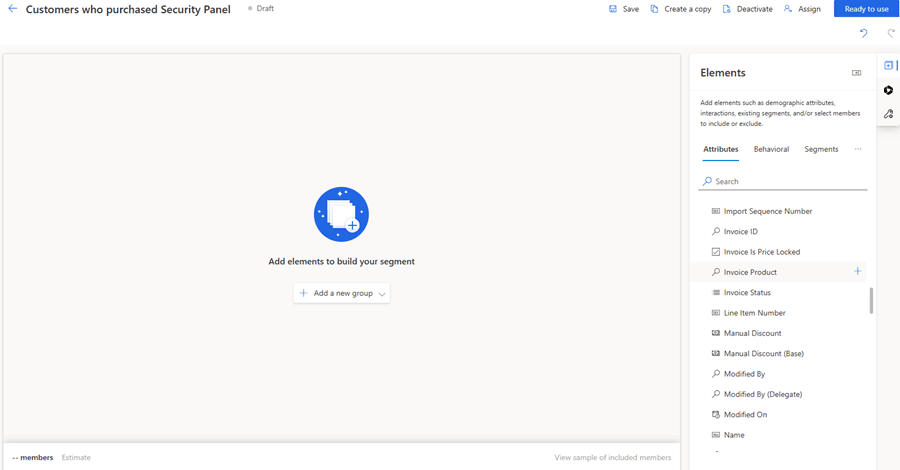
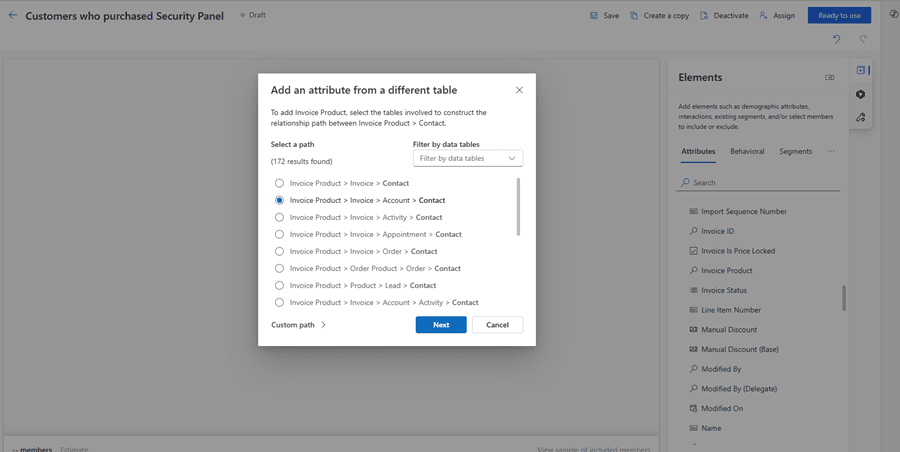
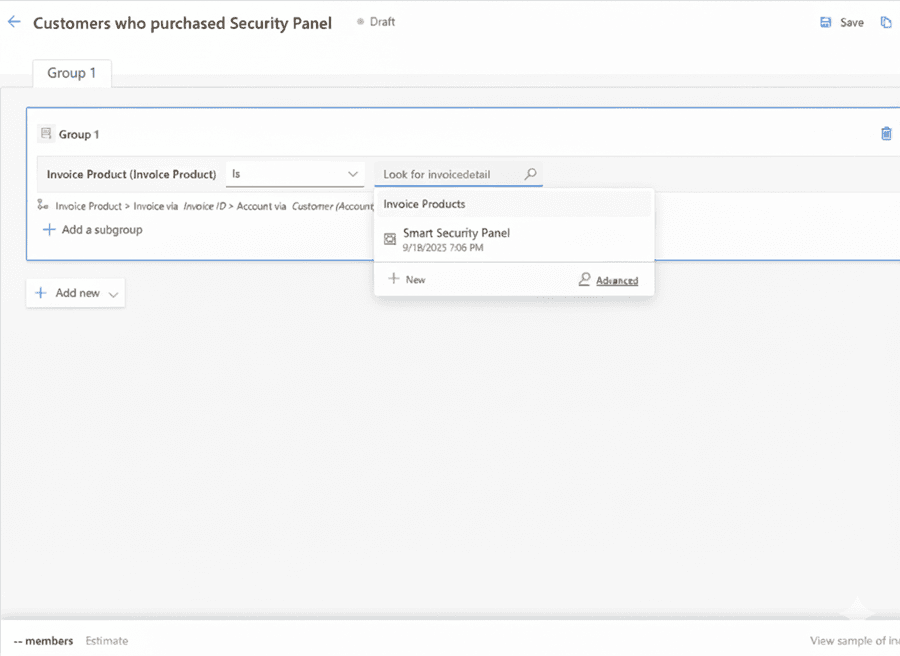
Preview & Activate
At the bottom of the screen, select Estimate and then Review Audience Preview to confirm that the segment returns the correct customers. After verifying the results, click Save and Go Live to activate the segment.
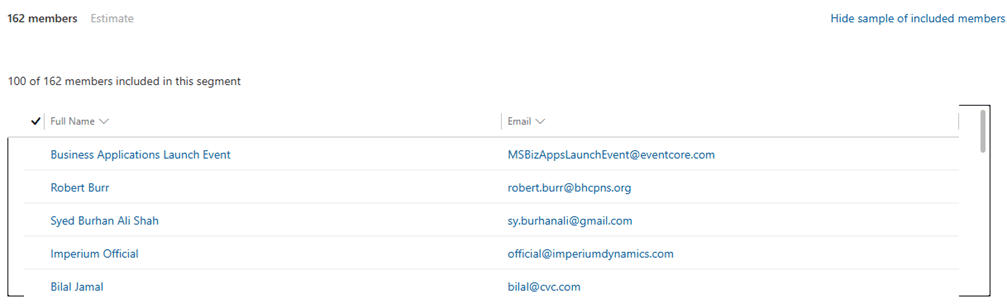
Key Considerations and Real-World Scenarios for Effective Segmentation in Dynamics 365 Customer Insights
What this section covers
This section highlights practical segmentation challenges encountered during real implementations and explains the strategies used to resolve them. Each scenario reflects how Dynamics 365 Customer Insights behaves in real environments and how thoughtful design, dynamic filters, helper attributes, and nested logic can overcome platform limits and create accurate and scalable segments for journeys and campaigns.
Consideration: Handling Multi-Value Effectively
Dynamics 365 Customer Insights offers flexible filtering capabilities, but working with extremely large data ranges, such as thousands of zip codes or large category lists, can slow down segment creation and increase the risk of manual error. Designing helper attributes or using calculated fields improves performance and makes segments significantly easier to maintain.
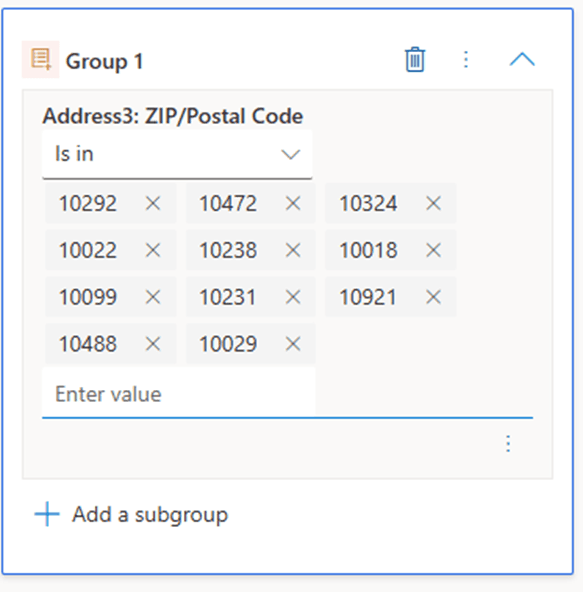
Scenario: Automating Segmentation for a Large Regional Audience
A company needed to create a segment for all customers living within the tri-state region of New York. The region included more than 10,000 ZIP codes, making the “IS IN” operator impossible to manage manually. Entering ZIP codes one by one would have been time consuming, inaccurate, and impractical for the marketing team.
To solve this, the company introduced a helper attribute called Tri State Region.
This attribute was enriched and populated automatically through a business rule that mapped each customer’s ZIP code to the correct region. As a result:
Every customer was automatically assigned to the correct tri state classification
New customers were mapped in real time as they entered the system
The segment required only one filter: Tri State Region = True
The team no longer had to maintain or update long ZIP code lists
This approach transformed the process from manual data entry to automated segmentation, improving speed and accuracy.
Why This Approach Is Effective
Scalable: The helper attribute supports large datasets and can easily be extended to new regions or categories without adjusting the segment filters.
Accurate: Automated mapping reduces data handling mistakes and ensures customers are assigned correctly based on ZIP code logic.
Efficient: Marketers can create regional or geographic segments quickly without dealing with thousands of values or complicated filters.
Maintainable: The business logic is stored in one place rather than inside multiple segmentation rules, making ongoing updates simple and centralized.
Consideration: Dynamic Recurring Email Segmentation
Audience targeting often depends on time-based conditions such as anniversaries, renewal cycles, or join dates. In these situations, it is best to use dynamic segments that update automatically. Dynamic segmentation reduces manual work, avoids maintaining multiple static lists, and ensures audiences stay accurate as new data enters the system.
This is especially important in customer journey automation, recurring email campaigns, and lifecycle marketing.
Scenario: Sending Recurring Emails Based on Employee Join Month
A common operational challenge occurs when organizations want to send annual surveys, reminders, or employee engagement emails based on the month an employee joined the company. For example:
Employees who joined in November should receive an email every November
Employees who joined in December should receive an email every December
And so on for all twelve months
In Dynamics 365 Customer Insights, there is no direct way to create a dynamic segment that filters only by the month portion of a date. While CI supports relative date filters and full-date comparisons, it does not provide month-only logic for recurring segmentation.
This creates a gap for teams running recurring journeys, anniversary-based campaigns, or employee lifecycle communications.
The Current Best Practice in Customer Insights and Marketing
To achieve month-based recurring segmentation, organizations often use the following approach:
Create twelve separate segments, one for each joining month
Create twelve separate journeys in Dynamics 365 Marketing, each scheduled for the correct month
Use helper attributes or calculated fields to make month filtering easier inside each segment
This approach works reliably and ensures employees receive emails at the right time. It also provides flexibility to fine-tune messages for specific months. While it requires some ongoing attention to keep multiple segments and journeys aligned, it remains a solid, dependable solution for recurring campaigns, anniversary notifications, and employee lifecycle communications.
Consideration: Filtering Contacts Who Have Never Received an Email
In many marketing platforms, excluding contacts who have never received an email is simple. In Dynamics 365 Customer Insights, however, there is no direct condition for “email never sent.” Instead, marketers must rely on behavioral attributes, activity history, and logical exclusions to identify contacts with zero email interactions.
This limitation often becomes noticeable in email marketing, audience cleansing, and engagement-based segmentation.
Scenario: Identifying Contacts with Zero Email History
A frequent requirement in marketing operations is to find contacts who have never received any marketing email. Platforms such as HubSpot provide a straightforward filter like “Email never sent.”
In Customer Insights, this requirement can be met through the following steps:
Use the Email Sent behavioral activity (or equivalent email-send event)
Set the timeframe to a very large range such as the last 100 years to ensure all historical activity is included
Apply a but not condition so that any contact with at least one email sent is excluded from the result
This combination effectively returns all contacts who have no email-send events associated with them.
Consideration: Using Nested Segments for Combined Criteria
Nested segments allow teams to build modular building blocks that can be reused across multiple segments and journeys. They simplify maintenance by allowing smaller and more focused segments to be combined into unified audiences. This improves scalability and consistency across marketing and service operations.
Platform Limitation
Dynamics 365 Customer Insights supports only one level of nested segmentation. Nested segments cannot be nested again. This means:
Users can use base segments inside a nested segment
Users cannot take a nested segment and include it in another nested segment
Any additional combinations must be built from base segments
Marketers must plan segmentation structures carefully to stay within this limitation.
Scenario: Customers with example.com Domain Residing in Seattle
In this example, two base segments are first created: one for customers with the example.com email domain and another for customers residing in Seattle. A third segment is then created as a nested segment, combining the two base segments. The resulting audience includes only customers who satisfy both conditions.
This approach is flexible and can be applied to many scenarios. Using nested segments makes segmentation modular, scalable, and easier to maintain, and it allows marketers to quickly adapt to new targeting needs without redefining filters from scratch. Nested segments are especially useful for audience reuse, behavioral and demographic targeting, and data-driven marketing strategies.
To illustrate this in practice, let’s walk through a simple example. First, create the segment for customers with the example.com email domain. Next, create the segment for customers residing in Seattle. Finally, combine these two base segments into a nested segment, which shows only customers who meet both criteria.
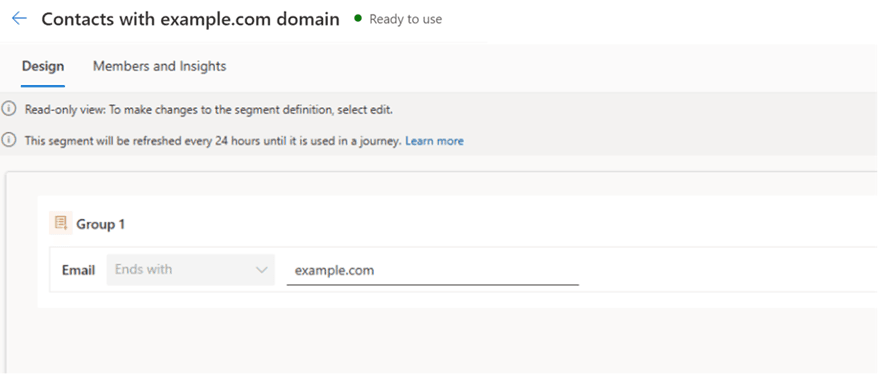
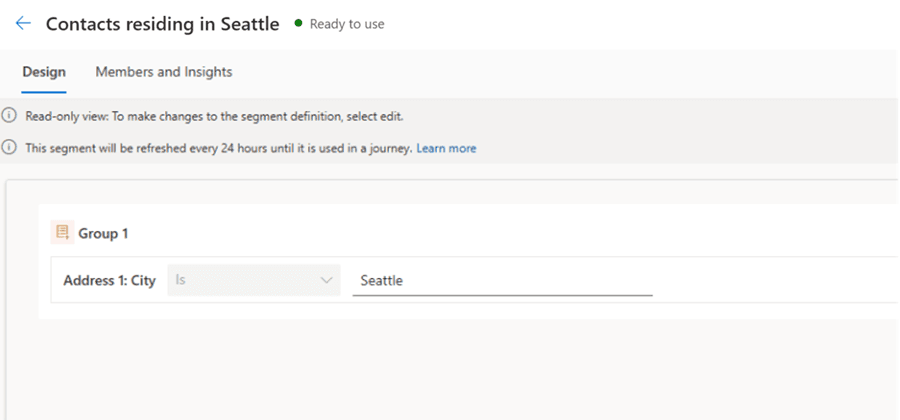
Next, create a new segment, then from the side pane, navigate to Segments and select the base segments which need to be included.

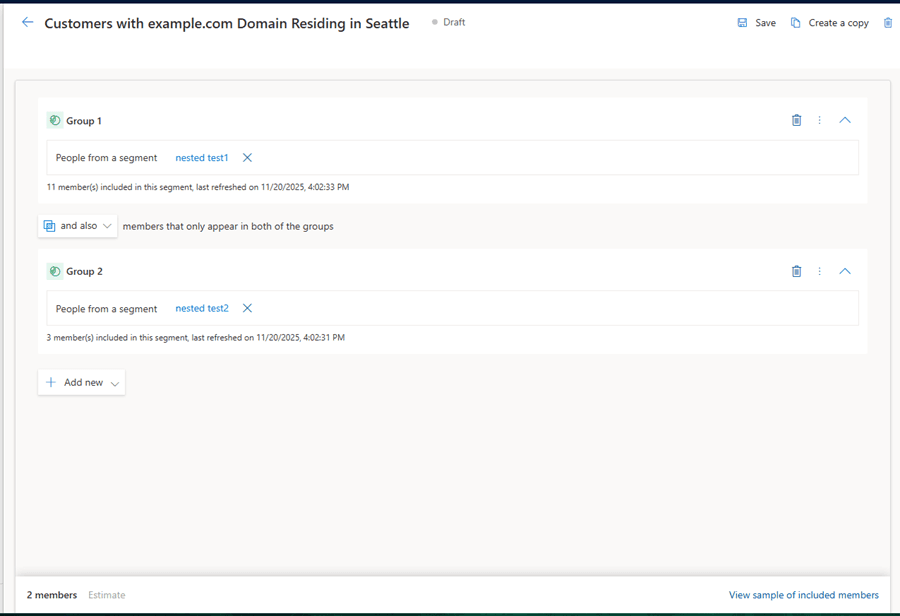
The screenshot shows the nested segment combining two base segments. The first segment includes customers with the example.com email domain, showing 11 members, and the second segment includes customers residing in Seattle, showing 3 members. Using the and also condition, the nested segment includes only customers who meet both criteria, resulting in 2 members. Depending on needs, users can also use Or to include members from either segment or But Not to exclude a segment.
Limitations & Best Practices
Limitations:
Nested segments cannot be referenced in other segments. Multi-level nesting is not supported and must be handled by creating additional base segments or applying alternative logic.
Filtering Contacts Without Prior Emails: Customer Insights does not provide a direct filter for contacts who have never received an email. Workarounds using behavioral attributes, email activity history, and logical conditions are required, which can be less intuitive and more complex.
Segment Refresh Frequency: Dynamic segments refresh on a scheduled cycle, while static segments require manual refresh. This can cause short delays for rapidly changing data or real-time marketing scenarios.
Large Multi-Value Attributes: Handling large lists, such as thousands of ZIP codes, manually is impractical and error prone. Automation, helper attributes, or business rules are necessary for scalable audience management.
Segment and Measure Limits: The service allows a maximum of 1000 active segments and measures combined, so large implementations require periodic cleanup.
Performance Limits for Real-Time Journeys: Segments used to start real-time journeys cannot exceed 10 million members due to platform performance policies.
Best Practices:
Use relative dates or criteria instead of hard-coded values. This allows segments to automatically adjust over time, for example, capturing upcoming birthdays or anniversaries without manual updates.
Automate multi-value attributes using business rules or Power Automate. This reduces manual effort and ensures that segments remain accurate and scalable for large datasets.
Start with the most relevant primary entity when filtering on related records. This simplifies segment design and reduces complexity when traversing lookup paths.
Keep segments dynamic whenever possible. Dynamic filters, behavioral triggers, or related-record attributes help reduce maintenance and ensure the segment stays up to date.
Always preview the audience before activation. Estimating segment size and reviewing members helps ensure campaigns target the correct contacts and avoids errors downstream.
Key Takeaways & Resources
Key Takeaways:
Customer Insights becomes significantly more effective when segments are designed with clear logic, scalable structure, and dynamic filters. Attribute-based data, behavioral interactions, and related table information can all work together to create rich and precise audiences. By following recommended practices, organizations can build segments that support more accurate targeting, more consistent personalization, and better customer engagement outcomes.
Related Resources:
Posted on: 17 December 2025



